|
MySQL 5.6.14 Source Code Document
|
|
MySQL 5.6.14 Source Code Document
|
Go to the source code of this file.
Macros | |
| #define | BUF_READ_AHEAD_AREA(b) ut_min(64, ut_2_power_up((b)->curr_size / 32)) |
Modes used in read-ahead @{ | |
| #define | BUF_READ_IBUF_PAGES_ONLY 131 |
| #define | BUF_READ_ANY_PAGE 132 |
| #define | BUF_READ_IGNORE_NONEXISTENT_PAGES 1024 |
Functions | |
| UNIV_INTERN ibool | buf_read_page (ulint space, ulint zip_size, ulint offset) |
| UNIV_INTERN ibool | buf_read_page_async (ulint space, ulint offset) |
| UNIV_INTERN ulint | buf_read_ahead_random (ulint space, ulint zip_size, ulint offset, ibool inside_ibuf) |
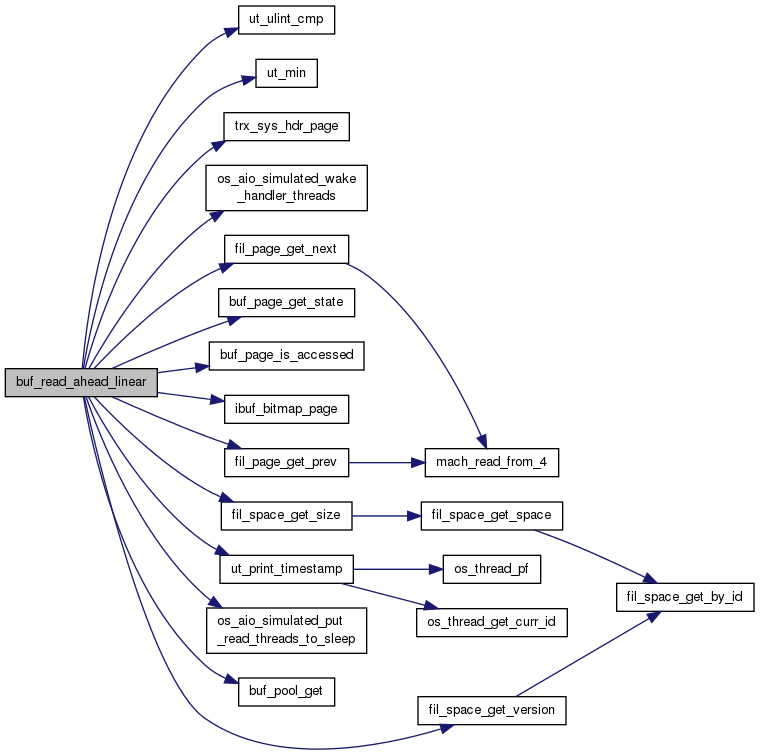
| UNIV_INTERN ulint | buf_read_ahead_linear (ulint space, ulint zip_size, ulint offset, ibool inside_ibuf) |
| UNIV_INTERN void | buf_read_ibuf_merge_pages (bool sync, const ulint *space_ids, const ib_int64_t *space_versions, const ulint *page_nos, ulint n_stored) |
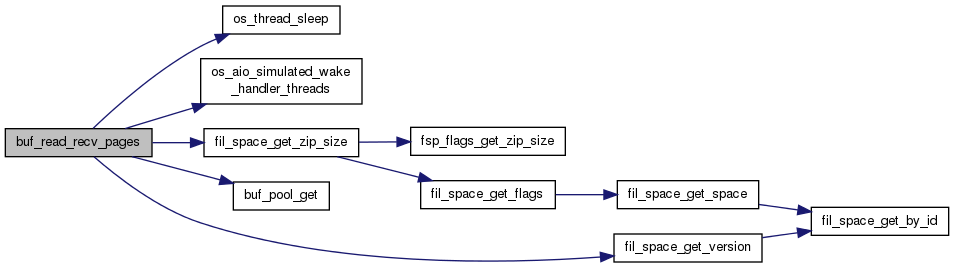
| UNIV_INTERN void | buf_read_recv_pages (ibool sync, ulint space, ulint zip_size, const ulint *page_nos, ulint n_stored) |
| #define BUF_READ_AHEAD_AREA | ( | b | ) | ut_min(64, ut_2_power_up((b)->curr_size / 32)) |
| #define BUF_READ_IBUF_PAGES_ONLY 131 |
| #define BUF_READ_IGNORE_NONEXISTENT_PAGES 1024 |
| UNIV_INTERN ulint buf_read_ahead_linear | ( | ulint | space, |
| ulint | zip_size, | ||
| ulint | offset, | ||
| ibool | inside_ibuf | ||
| ) |
Applies linear read-ahead if in the buf_pool the page is a border page of a linear read-ahead area and all the pages in the area have been accessed. Does not read any page if the read-ahead mechanism is not activated. Note that the algorithm looks at the 'natural' adjacent successor and predecessor of the page, which on the leaf level of a B-tree are the next and previous page in the chain of leaves. To know these, the page specified in (space, offset) must already be present in the buf_pool. Thus, the natural way to use this function is to call it when a page in the buf_pool is accessed the first time, calling this function just after it has been bufferfixed. NOTE 1: as this function looks at the natural predecessor and successor fields on the page, what happens, if these are not initialized to any sensible value? No problem, before applying read-ahead we check that the area to read is within the span of the space, if not, read-ahead is not applied. An uninitialized value may result in a useless read operation, but only very improbably. NOTE 2: the calling thread may own latches on pages: to avoid deadlocks this function must be written such that it cannot end up waiting for these latches! NOTE 3: the calling thread must want access to the page given: this rule is set to prevent unintended read-aheads performed by ibuf routines, a situation which could result in a deadlock if the OS does not support asynchronous io.
Applies linear read-ahead if in the buf_pool the page is a border page of a linear read-ahead area and all the pages in the area have been accessed. Does not read any page if the read-ahead mechanism is not activated. Note that the algorithm looks at the 'natural' adjacent successor and predecessor of the page, which on the leaf level of a B-tree are the next and previous page in the chain of leaves. To know these, the page specified in (space, offset) must already be present in the buf_pool. Thus, the natural way to use this function is to call it when a page in the buf_pool is accessed the first time, calling this function just after it has been bufferfixed. NOTE 1: as this function looks at the natural predecessor and successor fields on the page, what happens, if these are not initialized to any sensible value? No problem, before applying read-ahead we check that the area to read is within the span of the space, if not, read-ahead is not applied. An uninitialized value may result in a useless read operation, but only very improbably. NOTE 2: the calling thread may own latches on pages: to avoid deadlocks this function must be written such that it cannot end up waiting for these latches! NOTE 3: the calling thread must want access to the page given: this rule is set to prevent unintended read-aheads performed by ibuf routines, a situation which could result in a deadlock if the OS does not support asynchronous io.
| space | in: space id |
| zip_size | in: compressed page size in bytes, or 0 |
| offset | in: page number; see NOTE 3 above |
| inside_ibuf | in: TRUE if we are inside ibuf routine |
Definition at line 498 of file buf0rea.cc.
| UNIV_INTERN ulint buf_read_ahead_random | ( | ulint | space, |
| ulint | zip_size, | ||
| ulint | offset, | ||
| ibool | inside_ibuf | ||
| ) |
Applies a random read-ahead in buf_pool if there are at least a threshold value of accessed pages from the random read-ahead area. Does not read any page, not even the one at the position (space, offset), if the read-ahead mechanism is not activated. NOTE 1: the calling thread may own latches on pages: to avoid deadlocks this function must be written such that it cannot end up waiting for these latches! NOTE 2: the calling thread must want access to the page given: this rule is set to prevent unintended read-aheads performed by ibuf routines, a situation which could result in a deadlock if the OS does not support asynchronous i/o.
Applies a random read-ahead in buf_pool if there are at least a threshold value of accessed pages from the random read-ahead area. Does not read any page, not even the one at the position (space, offset), if the read-ahead mechanism is not activated. NOTE 1: the calling thread may own latches on pages: to avoid deadlocks this function must be written such that it cannot end up waiting for these latches! NOTE 2: the calling thread must want access to the page given: this rule is set to prevent unintended read-aheads performed by ibuf routines, a situation which could result in a deadlock if the OS does not support asynchronous i/o.
| space | in: space id |
| zip_size | in: compressed page size in bytes, or 0 |
| offset | in: page number of a page which the current thread wants to access |
| inside_ibuf | in: TRUE if we are inside ibuf routine |
Definition at line 237 of file buf0rea.cc.
| UNIV_INTERN void buf_read_ibuf_merge_pages | ( | bool | sync, |
| const ulint * | space_ids, | ||
| const ib_int64_t * | space_versions, | ||
| const ulint * | page_nos, | ||
| ulint | n_stored | ||
| ) |
Issues read requests for pages which the ibuf module wants to read in, in order to contract the insert buffer tree. Technically, this function is like a read-ahead function. in: number of elements in the arrays
Issues read requests for pages which the ibuf module wants to read in, in order to contract the insert buffer tree. Technically, this function is like a read-ahead function.
| sync | in: true if the caller wants this function to wait for the highest address page to get read in, before this function returns |
| space_ids | in: array of space ids |
| space_versions | in: the spaces must have this version number (timestamp), otherwise we discard the read; we use this to cancel reads if DISCARD + IMPORT may have changed the tablespace size |
| page_nos | in: array of page numbers to read, with the highest page number the last in the array |
| n_stored | in: number of elements in the arrays |
Definition at line 760 of file buf0rea.cc.
| UNIV_INTERN ibool buf_read_page | ( | ulint | space, |
| ulint | zip_size, | ||
| ulint | offset | ||
| ) |
High-level function which reads a page asynchronously from a file to the buffer buf_pool if it is not already there. Sets the io_fix flag and sets an exclusive lock on the buffer frame. The flag is cleared and the x-lock released by the i/o-handler thread.
High-level function which reads a page asynchronously from a file to the buffer buf_pool if it is not already there. Sets the io_fix flag and sets an exclusive lock on the buffer frame. The flag is cleared and the x-lock released by the i/o-handler thread.
| space | in: space id |
| zip_size | in: compressed page size in bytes, or 0 |
| offset | in: page number |
Definition at line 394 of file buf0rea.cc.
| UNIV_INTERN ibool buf_read_page_async | ( | ulint | space, |
| ulint | offset | ||
| ) |
High-level function which reads a page asynchronously from a file to the buffer buf_pool if it is not already there. Sets the io_fix flag and sets an exclusive lock on the buffer frame. The flag is cleared and the x-lock released by the i/o-handler thread.
High-level function which reads a page asynchronously from a file to the buffer buf_pool if it is not already there. Sets the io_fix flag and sets an exclusive lock on the buffer frame. The flag is cleared and the x-lock released by the i/o-handler thread.
| space | in: space id |
| offset | in: page number |
Definition at line 437 of file buf0rea.cc.
| UNIV_INTERN void buf_read_recv_pages | ( | ibool | sync, |
| ulint | space, | ||
| ulint | zip_size, | ||
| const ulint * | page_nos, | ||
| ulint | n_stored | ||
| ) |
Issues read requests for pages which recovery wants to read in. in: number of page numbers in the array
Issues read requests for pages which recovery wants to read in.
| sync | in: TRUE if the caller wants this function to wait for the highest address page to get read in, before this function returns |
| space | in: space id |
| zip_size | in: compressed page size in bytes, or 0 |
| page_nos | in: array of page numbers to read, with the highest page number the last in the array |
| n_stored | in: number of page numbers in the array |
Definition at line 836 of file buf0rea.cc.